Describe the Path of Lymph Circulation
Describe both systemic and pulmonary circulation. From there it goes to lymph nodes throughout the body as well as the spleen and antibodies are made.

How The Lymph System Pumps With No Pump Biological Strategy Asknature
Fluid that is forced out of the bloodstream during normal circulation is filtered through lymph nodes to remove bacteria abnormal cells and other matter.

. Lymph is the fluid in the lymphatic system. Some of the vaccine is absorbed through local capillaries into systemic circulation. Lymph circulation The flow of lymph from the tissues into the lymphatic collecting system.
Compare arteries and veins in terms of the direction of blood flow in relation to the heart. Antigen reaches lymphatic tissues and interacts with T-cells and B-cells. The lymphatic system contains two types of lymphoid tissues.
Allows diffusion of tissue fluid from interstitial spaces into the lymphatic pathway. The functions of the lymphatic system complement. The lymph flows from the vessels to trunk and then to collecting ducts.
The heart plays role in maintaining circulation throughout the body. Lymph consists of tissue fluid fats antibodies and cellular debris and moves by action of skeletal. Lymph flows from lymphatic vessels into lymphatic trunks and finally into collecting ducts where the lymph is disposed into the subclavian veins.
Lymphatic pathway Tissue fluid is transported from lymphatic capillaries to lymphatic collecting vessels where along the length of these vessels lymph nodes occur to filter the lymph and valves occur to prevent backflow of lymph. It is also defined as a network of tissues and organs that help to get rid of the toxins waste and other unwanted materials from the body. Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to pump it its upward movement depends on the motions of the muscle and joint pumps.
Lymphatic circulation The lymph is moved through the body in its own vessels making a one-way journey from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck. Pathogens are then filtered and screened by immune cells within the node. The lymphatic system is an elaborate network of vessels that act harmoniously to pump fluid and cells collectively called lymph from the interstitial space into the blood circulation.
Heaviness strong tingling persistent cramps intense itching skin tension. It plays role in transferring the fluid back to central circulation. Absorb fats from digestion 10.
This fluid is then transported back into the bloodstream via. Lymphatic system is considered as a part of both the circulatory and immune systems as well as a usually neglected part of students books. Define lacteal explaining its location and function.
Name and briefly describe the two subsystems of the circulatory system. I vmnhatie calls structures and oreans and 2. Begins with blind-ending capillaries containing one-way mini valves at the terminus into which excess interstitial fluid flows as pressure builds up in the tissue.
Fluid and immune cells move across the walls of specialised blood vessels which include high. APC carries antigen to local lymph nodes and enter lymphatic circulation. Occasional cramps especially at night tingling sometimes itching can be confused with other pathologies.
Heaviness cramps itching increasingly persistent especially during the evening 3rd STAGE. Absorb excess tissue fluid 3. The primary lymphoid tissue includes bone marrow and the thymus.
About Us Trending Popular Contact. Lymph flows from lymphatic vessels into lymphatic trunks and finally intocollecting ducts. Describe the composition of lymph fluid where it originates and how it is moved through lymphatic veins.
Trace the path of blood through pulmonary circulation. The lymphatic system is a system of specialized vessels and organs whose main function is to return the lymph from the tissues back into the bloodstream. The journey of lymph begins with the extravasation of fluid and cells from the blood capillaries into the interstitium.
The lymphatic system is a circulatory system for lymphatic fluid comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry the fluid in one direction toward the heart. Its functions include providing sites for certain immune system functions and facilitating plasma circulation in the cardiovascular system. Up to 24 cash back 9.
Run parallel to blood capillaries in all body tissues. Lymph from peripheral tissues is pumped into lymph nodes by afferent collecting lymphatic vessels. It is collected into.
The lymphatic capillaries join to form larger vessels with valves to ensure a one-way flow of. The oxygenated blood from the lungs leaves the pulmonary circulation when it enters the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Bone marrow contains the hematopoietic stem cells HSC that differentiate and mature into the various types of blood cells and lymphocytes see Figure 1 in Cellular DefensesThe secondary lymphoid tissues include the spleen lymph.
Fatty lymph picked up by the lacteals in the small intestine travels through the trunk into the duct and empties into venous circulation at the junction of the veins. Describe the structure of a vein. 49-9 Trace the path of blood through systemic circulation.
The lymph is transferred into subclavian veins. The lymphatic system is an elaborate network of vessels that collects the interstitial fluid or tissue fluid along with some protein molecules and drains it back into the major veins. Lymph is formed from the tissue fluid that fills the interstitial spaces of the body.
From the LV blood is pumped through the. The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport and immune response and disease resistance. Describe three main functions of the lymphatic system.
The lymph is a fluid that moves through a system of lymph vessels and nodes. Describe the path of lymph circulation Expert Answer Question Compare and contrast whole blood plasma interstitial fluid and lymph Solution The lymph is a water fluid that does not contain RBCs Its located in closed circulatory loop due to being too large to pass capillary membrane. The blood is then pumped through the mitral valves into the left ventricle LV.
Quick overview of the lymphatic system and how lymph flows through the body. View the full answer. Lymph flow is governed by extrinsic forces due to the movements of organs and skeletal muscles which.
The lymphatic system a complex network of vessels is essentially a drainage system within the body which transports excess fluid and metabolic waste products from interstitial spaces into the blood circulatory system.
How Lymphatic Vessels Move Fluid Video Khan Academy

Lymph Flow Pathway A Lymph Flow Pathway From Formation In The Download Scientific Diagram
How Does Lymph Move Through The Lymphatic System Socratic
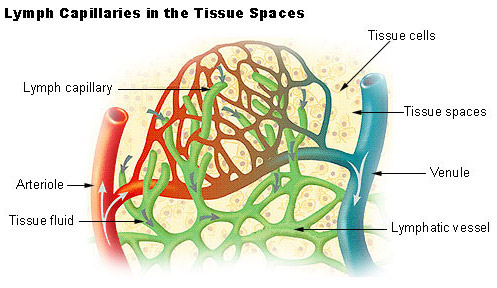
Seer Training Components Of The Lymphatic System
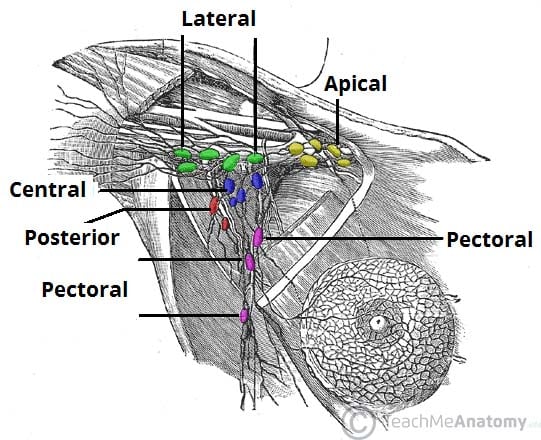
Lymphatic Drainage Of The Upper Limb Vessels Nodes Teachmeanatomy
Biol 238 Class Notes The Lymphatic System
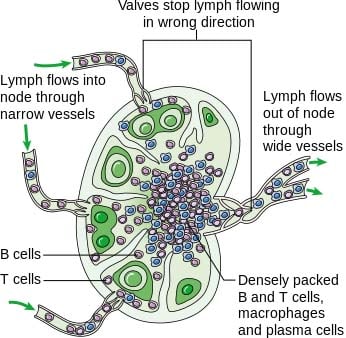
The Lymphatic System Vessels Nodes Organs Teachmeanatomy

Anatomy Of The Circulatory And Lymphatic Systems Microbiology

Pin On Pulmonary Embolism Survivor Massive Bilateral
Biol 238 Class Notes The Lymphatic System

Anatomy Of The Lymphatic And Immune Systems Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Lymph Drainage Along The Length Of The Mucosa Efferent Lymph From The Caudal Lymph Node Flows Into The Ile Thoracic Duct Lymph Drainage Lymphatic Drainage

Lymphatic Drainage An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

19 2c Lymph Transport Medicine Libretexts

Lymph Flow An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lymphatic System Lymphatic Pathways Of The Lymphatic System 15 02 Youtube

Lymphatic System Structure And Function Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
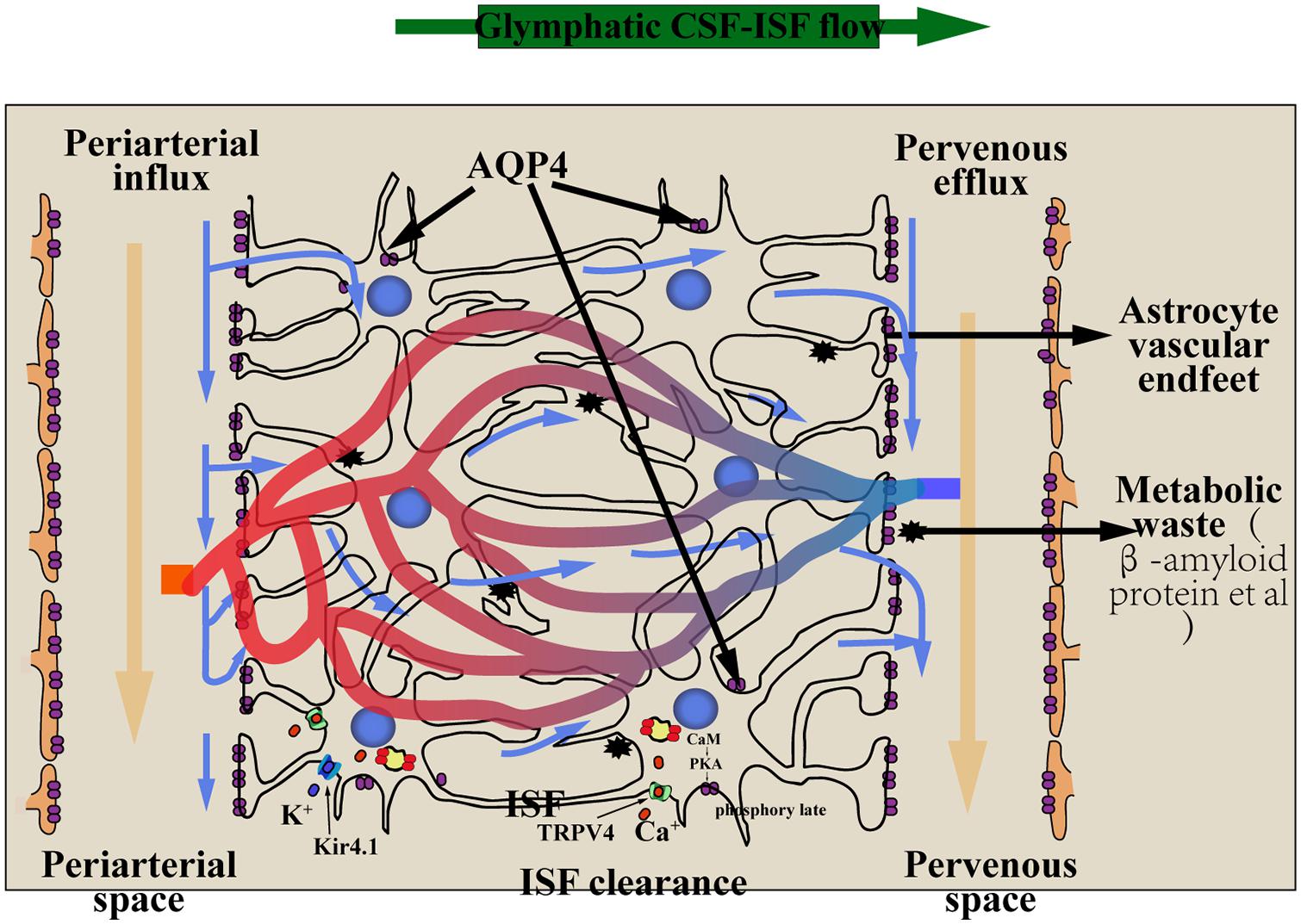
Frontiers Research On The Glial Lymphatic System And Its Relationship With Alzheimer S Disease Neuroscience
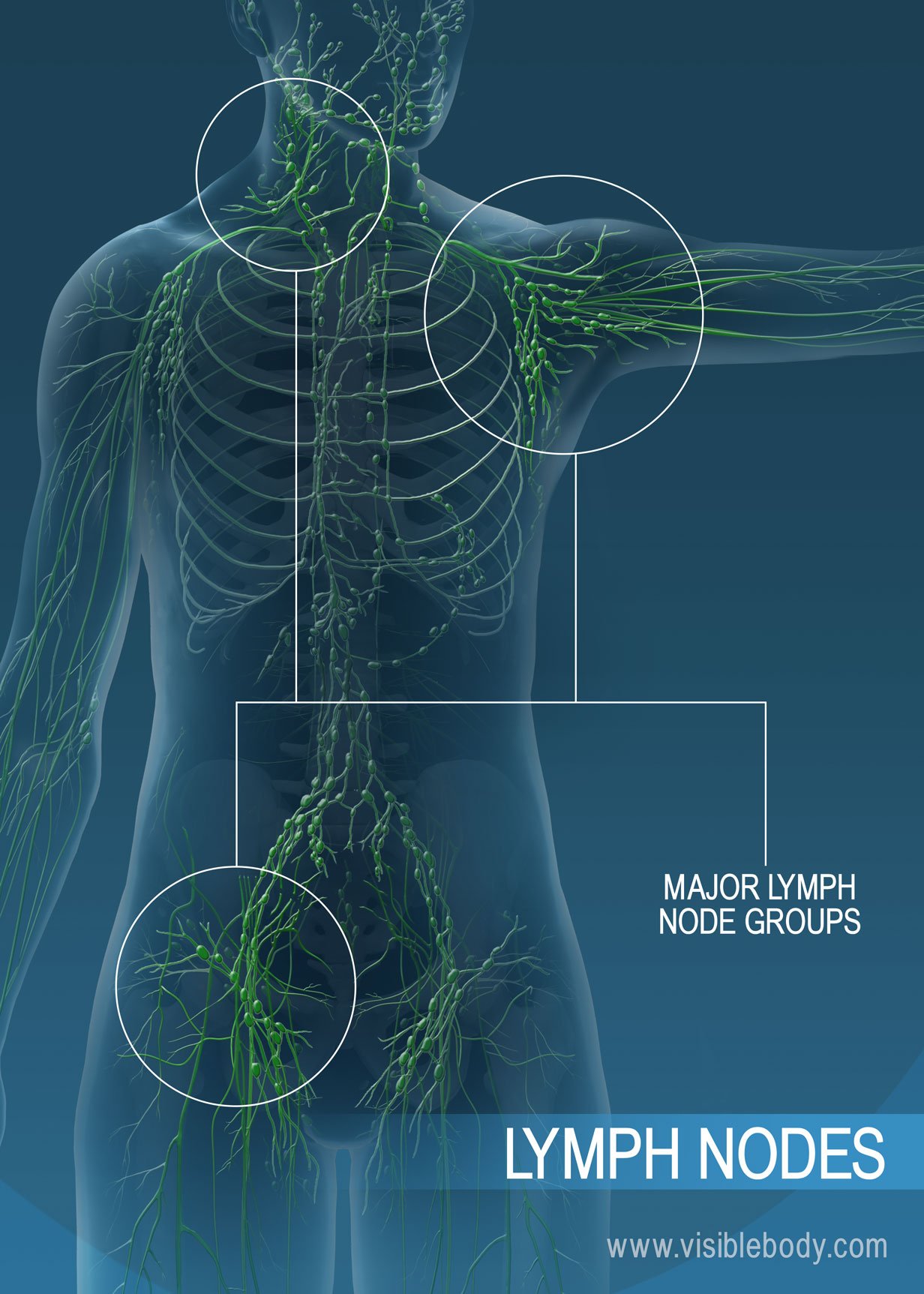
Comments
Post a Comment